Employee Training in the Age of IoT


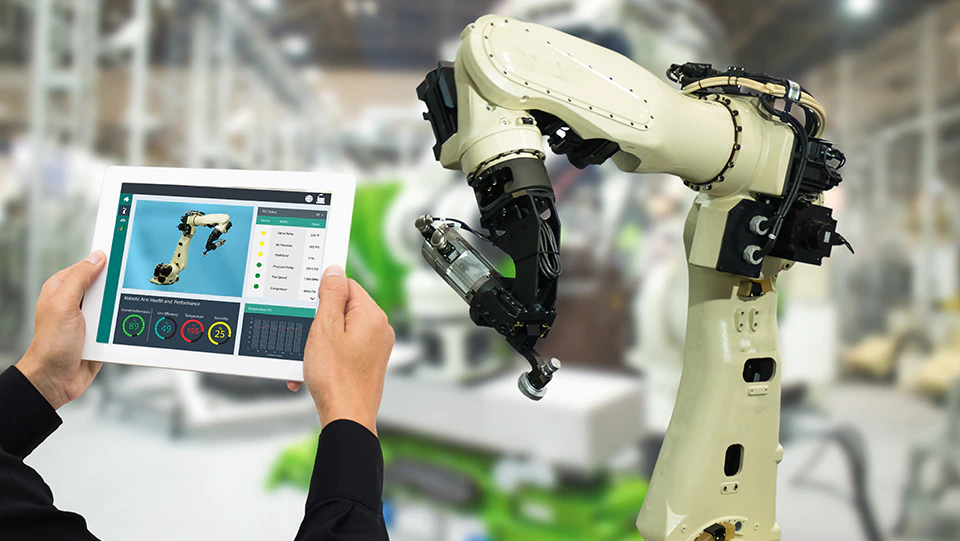
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming virtually every aspect of manufacturing. As manufacturers incorporate Industry 4.0 technology and increased automation into their facilities, focusing on training and developing employees continues to be a key component of a safe, efficient workplace. Are your employee training and safety programs keeping pace with manufacturing industry changes?
The incorporation of IoT devices in the workplace provides the opportunity for manufacturers to monitor and gather data and use that information to more closely manage the operations and resources of a facility. However, the introduction of new technology in the workplace can present new and still emerging risks. In addition to training employees to safely use and maintain high-tech equipment, manufacturers will also want to train employees not to become blindly reliant on new technologies and where applicable, how to interpret and act upon the feedback provided by newer devices.
For example, there are now wearables designed to provide direct responses to unsafe practices or proximate hazards. Imagine how effective this technology can be in reducing accidents, when the employees wearing them are well-versed on how to respond to the alerts coming from their devices.
“IoT can offer a competitive advantage to manufacturers,” said Erika Melander, Travelers Manufacturing INDUSTRYEdge® Manager. “Manufacturers can use operational data to help reduce downtime and increase efficiency and potentially reduce unsafe actions or conditions,” Melander said. “It does require an investment of time to train employees to properly use these devices and interpret and act on the data that they generate.”
What are the risks of IoT?
There are many risks to understand as the IoT evolves and machinery and equipment continue to incorporate connectivity. People may pose the greatest risk and at the same time can be its strongest deterrent, depending on how well prepared they are for the change to their operations. It is important for manufacturers to have a full understanding of the features of the IoT implemented on the equipment and machinery in their facility, particularly features designed to promote safety.
It is just as important for the manufacturer to ensure that employees working with or around IoT-enabled machinery or equipment understand how a device functions, its limitations and what reliability issues should be factored in, such as wireless connectivity. These require training.
Training for safety and understanding
Remember, management and employees may have a developed knowledge of traditional manufacturing equipment and legacy knowledge of conventional safety features. However, emerging IoT technology incorporating new or novel safety features can present new safety risks for employees. This is because they may lack familiarity with or simply misunderstand these features and the extent to which the features can or should be relied upon for safety. It’s important for management and employees to approach the adoption of new technologies with the mindset of safety and education first. Create a workplace protocol where, before implementation, training for a thorough understanding of new device features and their limitations is standard.
Consider these tips:
- Involve stakeholders. When customizing new IoT-enabled equipment for the factory floor, consider involving the stakeholders in the safe and efficient operation of the equipment. For example, engage the quality assurance manager, the safety manager, employees who will use the equipment, and maintenance workers to help evaluate potential risks and develop safe practices that can be further used for training others or identify other safeguards that may be needed should sensors or IoT safety features fail.
- Inform installers. Recognize that installers of IoT-enabled sensors may not be fully familiar with the plant machinery or systems that they are working with or how these are integrated into overall plant control systems. Ensuring that these third parties are knowledgeable of dependent systems may also require training. IoT-enabled equipment and machinery can present a manufacturer with a greater ability to monitor and ensure that the machinery is operating properly.
- Include IT staff. By incorporating IoT sensors, the reliability of wireless communication systems can be very important for general monitoring or critical alerts. For this reason, IT staff may also need to be trained on the dependencies of a network outage, for example.
How can data insights drive safety?
Manufacturers can leverage data and insights gathered in real time from IoT-enabled equipment and machinery. IoT presents manufacturers with the potential to detect maintenance needs and abnormalities during the operation of equipment, including potential misuse. Emerging IoT devices may offer new types of data and the analytical tools to identify problem areas or trends that were not understood before. As a result, preventive maintenance schedules or safe work practice instructions and the corresponding employee trainings may need to be updated. Incorporating IoT data into safety management systems can give manufacturers a better picture of their overall risks.
How is IoT improving employee safety?
IoT technology continues to introduce new safety features designed to help keep employees safe. Some of these features include:
- Wearable IoT devices equipped with proximity sensors to alert employees of approaching forklifts or other heavy machinery.
- Wearable motion monitors to identify high-risk bodily motions in real time, to help prevent sprains and strains.
- IoT sensors to detect levels of fatigue and provide an alert when vehicle or heavy equipment operators become drowsy, to help avoid accidents.
- Collaborative robots, designed to work safely alongside human workers, can perform repetitive or dangerous tasks. Intelligent sensors can reduce speed and torque when the robot detects the presence of humans.
Wearable IoT devices can also collect individualized data to establish risk profiles for individual employees to help identify areas where an employee may need additional training to safely perform tasks.
“These individualized risk profiles can allow manufacturers to be proactive with their safety training, rather than waiting for an incident,” said Melander. For example, IoT wearables worn on a job involving material handling can help reinforce what employees have learned during training, such as proper bending and lifting techniques, and help determine if corrective measures are effective.
How can training keep pace with change?
To help keep pace with change, manufacturers can incorporate their IoT initiatives into their corporate safety culture, from initial customization, to employee onboarding, to continued training and development of employees, to post incident responses. In 2017, the manufacturing industry saw an 84% increase in IoT network connections, more than any other industry surveyed.1 Industry analysts expect growth of new technology to continue. It’s not only new hires who need training. Current employees who are learning new tasks or are new to the IoT-enabled equipment or machinery can benefit from additional training on IoT devices. Knowing how to properly and safely operate IoT equipment and machinery, as well as learning from operational data, can help manufacturers increase safety and productivity.