How to Adjust Your Desk Chair and Workstation

Are you doing everything you can to be comfortable at work? There are some simple things you can do to help improve your comfort. To start, if you have never adjusted your desk chair, you may be putting some unnecessary stress on your body. Fortunately, there are some simple adjustments that you can make to your desk chair, your office space and your work habits that can help reduce stress on your body.
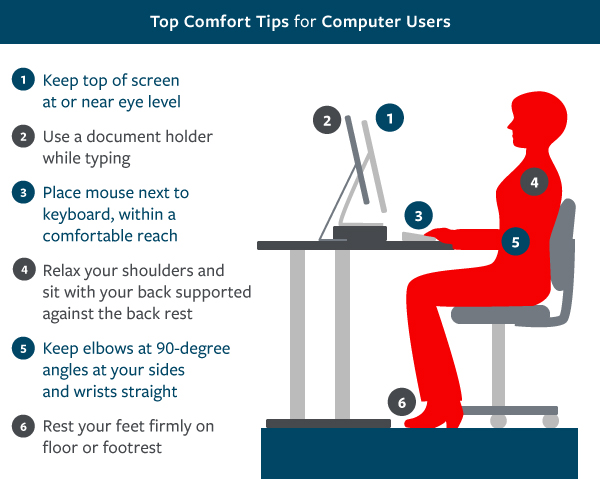
- Keep top of screen at or near eye level
- Use a document holder while typing
- Place mouse next to keyboard, within a comfortable reach
- Relax your shoulders and sit with your back supported against the back rest
- Keep elbow at 90-degree angles at your sides and wrists straight
- Rest your feet firmly on floor or footrest
Adjusting your chair:
- Your chair should have at least a five-point base, should be height adjustable as well as have an adjustable backrest and seat pan.
- Adjust the height of the chair's seat so your thighs are horizontal, feet rest flat on the floor, forearms are parallel with the floor, and hands are comfortably positioned at the keyboard.
- Adjust the chair back so it supports your lower back and fits the curvature of your spine. Adjust the seat pan for proper slope and comfort.
- Make sure the chair rolls freely on the floor.
- Position the armrests to allow your forearms to rest lightly on them.
Additional workstation adjustments:
- Position the keyboard at elbow height with your mouse next to your keyboard. Consider moving the mouse to the left side of your keyboard and use your left hand if you are reaching for the mouse when it is on the right hand side. You can do this periodically throughout the day or as an alternative to using your right hand.
- Consider learning and using keyboard shortcuts to reduce the amount you use your mouse.
- Make sure you are not resting your wrists when you type or use your mouse.
- Position the computer monitor so it is in line with your keyboard, with the top of the monitor near eye level and approximately an arm’s reach away. If you are using two monitors, you may need to place them a little farther than an arm’s reach to allow you to comfortably see each one.
- Arrange your workstation to easily access items you use often to avoid excessive reaching.
Other healthy work habits:
- Change work positions throughout the day. Periodically stretch your muscles in the back, legs, shoulders, neck, arms, wrists and fingers. Stand up and move about whenever possible.
- Look away from the monitor periodically and momentarily focus on a distant object while blinking. This is especially important after you have been concentrating on your computer for a long period of time.
- Have your vision checked and corrected regularly. Tell your eye doctor how much time you spend on the computer – both at the office and at home.
- Type softly on the keyboard while keeping your hands and fingers relaxed with your wrists in a neutral position. Do not rest your wrists when you type or use the mouse.
- Improve your physical fitness and flexibility by exercising and stretching regularly. (NOTE: Consult your physician before beginning any exercise or stretching program.)
Other ergonomic equipment:
- Position a document holder close to your computer screen and at the same level and distance from your eyes to avoid constant change of focus. You can also use the space between the monitor and keyboard tray. Consider using a three-ring binder (rings placed toward the monitor) as a document holder.
- Phone headsets can help reduce neck strain and improve posture.
- Footrests can provide additional comfort if your feet do not rest firmly on the floor. Consider a keyboard tray if your work surface or chair cannot be properly adjusted to position your elbow height at 90 degrees.



